Dr. Weibing Wang from Fudan University delivered a presentation on assessing the effectiveness and impact of vaccines using mathematical modeling. He introduced the motivation for conducting economic evaluations of vaccines and vaccination programs, outlined basic models and methods to measure the effectiveness and impact of infectious disease interventions, and discussed the advantages and limitations of different evaluation models of infectious disease interventions.
Dr. Hai Fang from Peking University presented the research regarding the economic analysis of introducing the Hib vaccine into China’s National Immunization Program. He concluded that it is cost-effective to introduce the Hib vaccine into China’s NIP at both national and provincial levels.
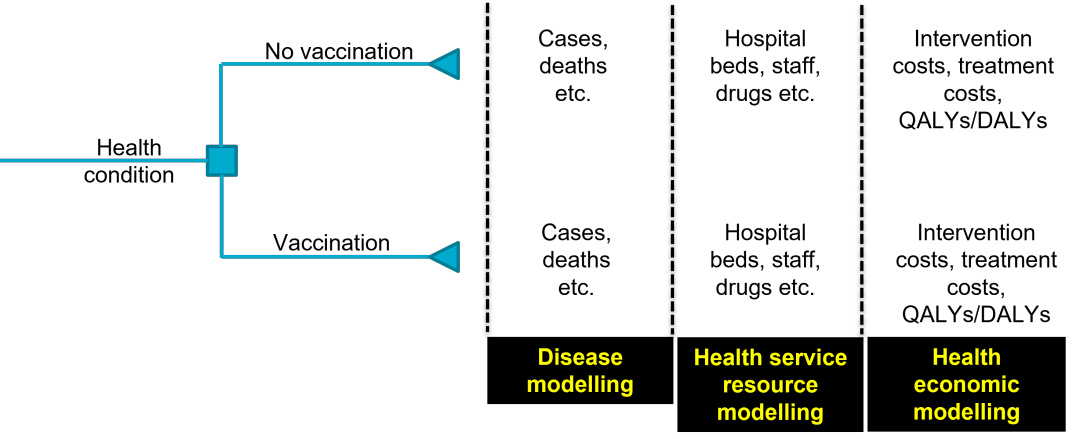
One international speaker, Dr. Mark Jit from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM), shared different types of models to evaluate the impact of vaccination, including mechanical and statistical models, dynamic and static models, agent-based models, and compartmental models.
Reference Research and Materials
1. Direct,indirect and total effects of 13-valent
pneumococcal conjugate vaccination on invasive pneumococcal disease in children in
Navarra, Spain, 2001 to 2014: cohort and case-control study (DOl:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2016.21.14.30186)
⒉. Effectiveness of inactivated and Ad5-nCoV COVID-19 vaccines
against SARS-CoV-2 0micron BA.2 variant infections, severe illness, and Death(DOl:10.1186/s12916-022-02606-8)
3. Effectiveness of inactivated COVID-19 vaccines among older adults inShanghai: retrospective cohort study (DOI:10.1038/s41467-023-37673-9)
4. lmpact of the national hepatitis B immunization program in China: a modeling study(DOI: 10.1186/s40249-022-01032-5)





