Streptococcus pneumoniae (Spn) is a lancet-shaped, Gram-positive, facultative anaerobic bacterium first identified in 18811. It is a major opportunistic pathogen that commonly colonizes the human nasopharynx, with colonization rates ranging from 27% to 65% in children and less than 10% in adults 1,2. Generally, it does not cause disease, depending on host characteristics and changes in the colonization environment1.
Spn is widely distributed in nature, with humans as its only host. It spreads from person to person, typically through respiratory droplets or by colonizing the upper respiratory tract, with infections more common in winter and early spring1. Although the infectious period of pneumococcal diseases is not well-defined, it is presumed that transmission can occur as long as the pathogen is present in respiratory secretions3.
Pneumococcal disease (PD) refers to a group of infections caused by Spn, categorized into invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) and non-invasive pneumococcal disease (NIPD) based on the site of infection4. NIPD is more common but often undiagnosed due to the lack of pathogen testing, whereas IPD, though less frequent, presents more severe symptoms and higher mortality risk5.
The migration of Spn to sterile tissues and organs is the main cause of all pneumococcal diseases6. Spn colonizing the nasopharynx can cause invasive infections if not cleared by the immune system7, leading to conditions like pneumonia, bacteremia, and meningitis.
Risk factors for IPD include immunosuppression due to disease or medication, functional or anatomical asplenia, chronic heart diseases, lung diseases (including asthma), liver or kidney diseases, smoking, alcoholism, cerebrospinal fluid leaks, cochlear implants, and attending day-care or other preschool childcare settings8.
Nearly 100 serotypes of Spn are known, most capable of causing disease. Approximately 62% of global IPD cases are attributed to the 10 most common serotypes6. The prevalent serotypes among carriers are also the primary causes of infections. While colonization does not always lead to disease, it is a critical prerequisite for PD9. Different serotypes may preferentially cause various diseases or conditions, such as asymptomatic colonization, meningitis, or pneumonia.
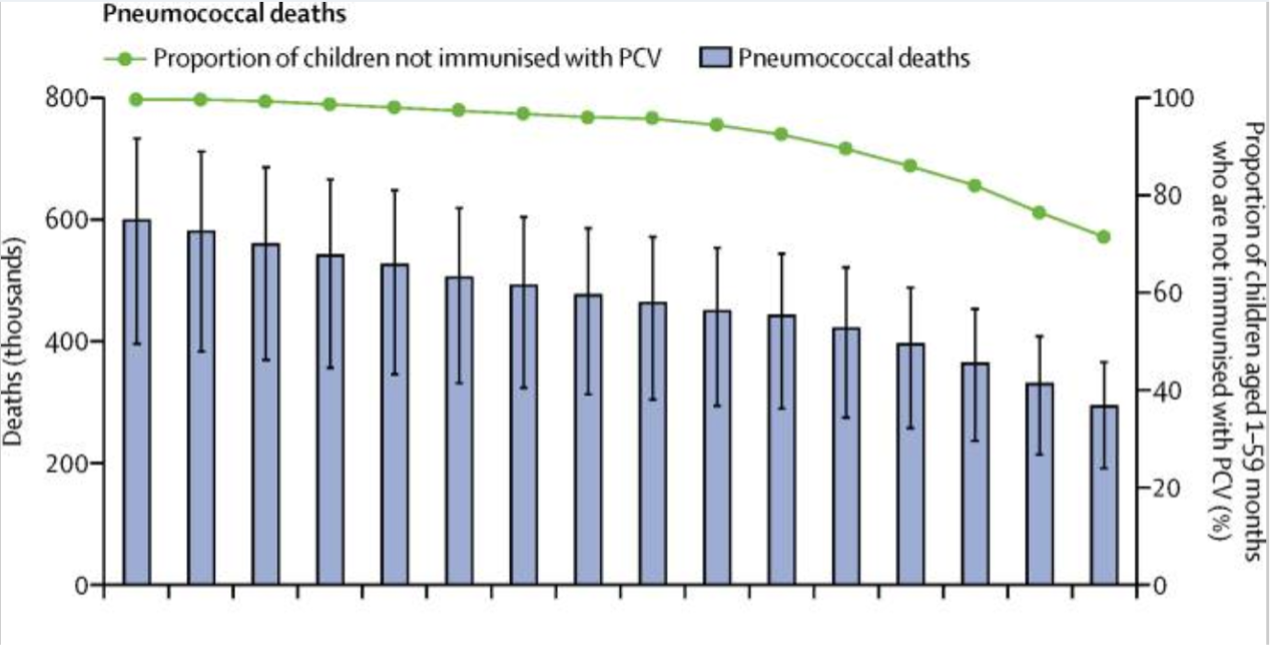
Pneumococcal deaths only include the HIV-negative deaths number. WHO/UNICEF adjusted the vaccine coverage estimates to present the proportion of children aged 1-59 months who have been vaccinated PCV. The Vertical lines indicate uncertainty intervals.
(Source: Wahl, B., O’Brien, K. L., Greenbaum, A., Majumder, A., Liu, L., Chu, Y., … & Cohen, A. L. (2018). Burden of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae type b disease in children in the era of conjugate vaccines: global, regional, and national estimates for 2000–15. The Lancet Global Health, 6(7), e744–e757.)
The distribution of pathogenic Spn serotypes varies by geography, age, and clinical presentation. Globally, the seven most common serotypes in children under five are 1, 5, 6A, 6B, 14, 19F, and 23F, accounting for over half of IPD cases10. A systematic review published in 2010 described the serotype distribution among children under five with IPD worldwide from 1980 to 2007 (Figure 2) 10. In Southeast Asia, the most common serogroups and serotypes among reported IPD cases are serogroup 19 (16.2%), serogroup 6 (14.6%), serogroup 23 (12.5%), serotype 14 (9.2%), serotype 1 (5.7%), and serotype 3 (4.0%)11. In China, a literature review from 1980 to 2008 indicated that serotypes 14, 19A, and 19F were most prevalent among pneumonia and meningitis cases in children under five12. Additionally, studies have found that the common serotypes causing IPD in children in mainland China include 19A, 19F, 14, 23F, and 6B13.
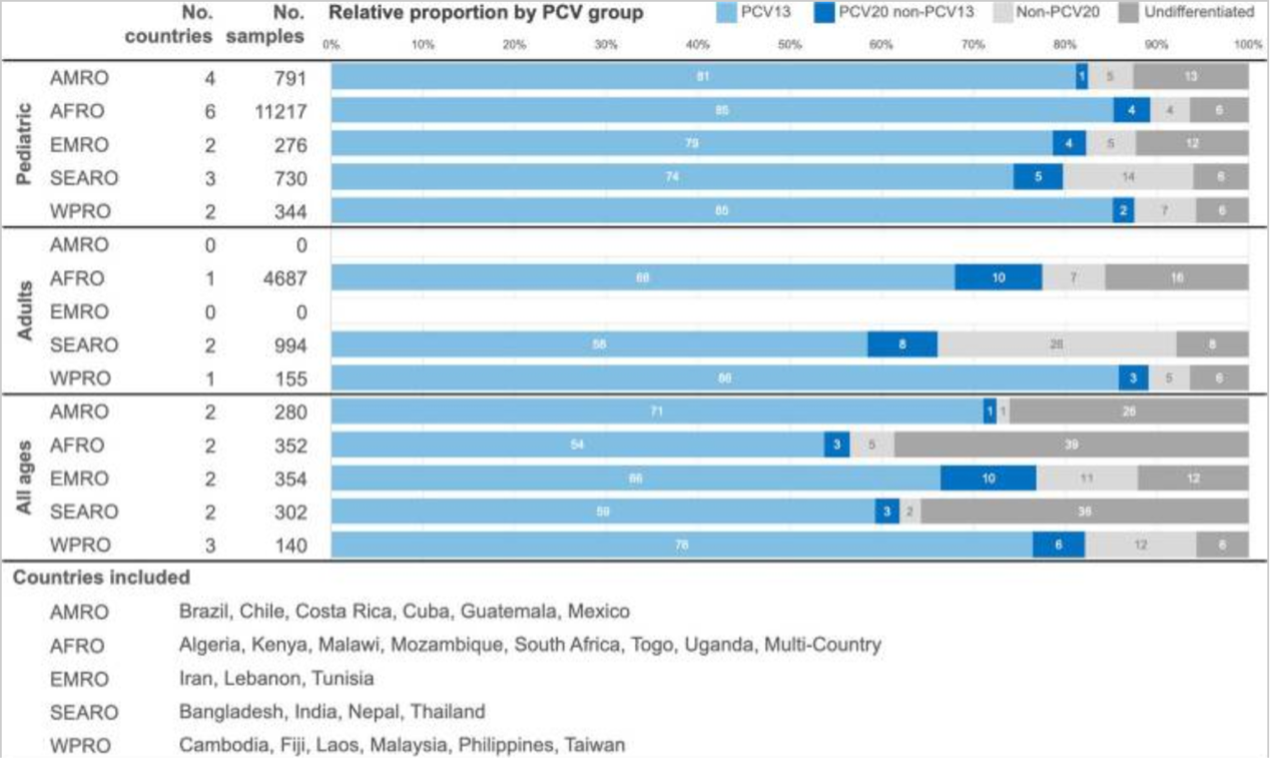
(Source: Fletcher, M. A., Daigle, D., Siapka, M., Baay, M., Hanquet, G., & Morales, G. D. C. (2024). Serotype distribution of invasive pneumococcal disease from countries of the WHO Africa, Americas, Eastern Mediterranean, South-East Asia, and Western Pacific regions: A systematic literature review from 2010 to 2021. Frontiers in Public Health, 12.)
Table 1 Distribution of PCV serotypes after inclusion of different doses of PCV vaccine in the immunization schedule
| WHO Region AMRO | Country/ Region | Age Group | Time Period | Enrollment Time | Study ID | Study Period | PCV13 Serotypes | PCV20 Serotypes (excluding PCV13) | Non-PCV20 Serotypes | Other Serotypes | Total Number |
| % | % | % | % | N | |||||||
| Argentina | Children | PCV | PCV13(2012) | 3860 | 2012-2013 | 62.7 | 11.9 | 7.5 | 13.4 | 67 | |
| 2012-2013 | 79.4 | 20.6 | 563 | ||||||||
| 1270 | 2015-2017 | 34.3 | 21.0 | 32.7 | 12.0 | 434 | |||||
| Adults | PCV-hv | PCV13(2012) | 1245 | 2013-2017 | 43.1 | 27.6 | 4.6 | 24.8 | 791 | ||
| Brazil | Children | PCV-hv | PCV10(2010) | 1828 | 2010-2012 | 72.0 | 9.8 | 17.8 | 0.3 | 325 | |
| 450 | 2011-2015 | 51.6 | 48.4 | 62 | |||||||
| 1270 | 2015-2017 | 46.7 | 18.1 | 29.7 | 5.4 | 441 | |||||
| Adults | PCV-hv | PCV10(2010) | 197 | 2013-2015 | 51.0 | 23.5 | 7.6 | 02 | |||
| All Ages | PCV-hv | PCV10(2010) | 748 | 2010-2012 | 61.6 | 14.5 | 19.5 | 4.4 | 159 | ||
| 121 | 2014-2015 | 47.5 | 19.9 | 25.0 | 7.4 | 1630 | |||||
| 120 | 2017-2019 | 44.6 | 7.2 | 36.8 | 1.5 | 2402 | |||||
| Chile | Children | PCV-hv | PCV10(2011) | 1127 | 2012-2012 | 60.4 | 1.1 | 38.5 | 91 | ||
| 1270 | 2015-2017 | 52.7 | 4.6 | 28.2 | 4.5 | 404 | |||||
| Colombia | Children | PCV-hv | PCV10(2011) | 1270 | 2015-2017 | 66.8 | 4.8 | 26.1 | 3.1 | 352 | |
| Adults Adults | PCV-hv | PCV10(2011) | 4034 | 2012-2019 | 48.1 | 4.2 | 37.7 | 310 | |||
| All Ages | PCV-hv | PCV10(2011) | 3267 | 2012-2017 | 56.9 | 11.4 | 31.6 | 0.1 | 842 | ||
| Dominican Republic | Children | PCV-hv | PCV13(2013) | 1270 | 2015-2017 | 67.2 | 3.4 | 19.0 | 10.3 | 58 | |
| All Ages | PCV-hv | PCV13(2013) | 3480 | 2013-2016 | 897 | 10.3 | 39 | ||||
| Mexico | Children | PCV-hv | PCV13(2011) | 270 | 2015-2017 | 41.2 | 18.3 | 32.0 | 8.5 | 153 | |
| Paraguay | Children | PCV-hv | PCV10(2011) | 1270 | 2015-2017 | 679 | 10.1 | 13.8 | 8.3 | 109 | |
| Peru | Children | Transitional Period | PCV7(2009 | 2009-2011 | 84.5 | 10.3 | 58 | ||||
| All Ages | Transitional Period | PCV7(2009) | 2136 | 2010-2011 | 64.6 | 15.2 | 15.2 | 2.5 | 79 | ||
| Uruguay | Children | PCV-hv | PCV13(2010) | 1270 | 2015-2017 | 43.7 | 9.5 | 29.9 | 6.9 | 87 | |
| All Ages | PCV-hv | PCV13(2010) | 348 | 2011-2012 | 46.1 | 53.9 | 356 | ||||
| Venezuela | Children | Hybrid Period | pre-PCV, PCV13(2014) | 1270 | 2006-2017 | 90.6 | 9.4 | 309 | |||
| AFRO | Burkina Faso | Children | PCV-hv | PCV13(2013) | 3356 | 2014a | 88.0 | 12.0 | 25 | ||
| 2017b | 50.0 | 7.1 | 42.9 | 14 | |||||||
| All Ages | PCV-hv | PCV13(2013) | 2320 | 2014-2015 | 72.7 | 8.1 | 3.3 | 15.8 | 377 | ||
| 3355 | 2016-2017 | 56.0 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 41.4 | 739 | |||||
| Cameroon | Hybrid Period | pre-PCV, PCV13(2011) | 1493 | 2010-2016 | 55.2 | 27.6 | 17.2 | 29 | |||
| PCV-hv | PCV13(2011) | 2536 | 2015-2018 | 35.8 | 17.0 | 30.2 | 17.0 | 53 | |||
| Ethiopia | All Ages | PCV-hv | PCV10(2011) | 2018-2019 | 37.1 | 5.7 | 28.6 | 28.6 | 35 | ||
| Gambia | Children | Hybrid Period | Pre-PCV, PCV7(2009), PCV13(2011) | 2575 | 1995-2016 | 63.1 | 17.7 | 19.2 | 203 | ||
| Ghana | All Ages | PCV-hv | PCV13(2012) | 2445 | 2015-201 | 69.5 | 0.2 | 3.4 | 16.9 | 59 | |
| 1497 | 2015-2017 | 71.5 | 28.5 | 137 | |||||||
| Kenya | Children | PCV-hv | PCV10(2011) | 400 | 2012-2016 | 26.8 | 73.2 | 82 | |||
| Madagascar | Children | PCV-hv | PCV10(2012) | 4041 | 2013-2018 | 19.5 | 1.1 | 37.9 | 41.4 | 87 | |
| Malawi | Children | Hybrid Period | Pre-PCV, PCV13(2011) | 2575 | 1995-2016 | 73.0 | 6.6 | 20.4 | 226 | ||
| All Ages | 多时期 | Pre-PCV, PCV13(2011) | 1407 | 2006-2018 | 54.5 | 45.5 | 1594 | ||||
| Mozambique | Children | PCV-hv | PCV10(2013) | 785 | 2013-2014 | 62.0 | 2.0 | 36.0 | 50 | ||
| 2870 | 2013-2015 | 71.0 | 29.0 | 69 | |||||||
| 695 | 2014-2015 | 70.0 | 3.3 | 20.0 | 6.7 | 30 | |||||
| Niger | All Ages | PCV-hv | PCV13(2014) | 2958 | 2016-2018 | 42.4 | 5.3 | 4.1 | 38.2 | 70 | |
| Nigeria | Children | Hybrid Period | Pre-PCV, PCV10(2014) | 1073 | 2010-2016 | 50.0 | 3.6 | 46.4 | 28 | ||
| Senegal | Children | Hybrid Period | Pre-PCV, PCV13(2013) | 3365 | 2010-2016 | 91.4 | 6.9 | 58 | |||
| South Africa | Children | PCV-hv | PCV13(2011) | 2575 | 2013-2014 | 28.2 | 31.6 | 39.9 | 0.3 | 291 | |
| All Ages | PCV-hv | PCV13(2011) | 3614 | 2012 | 53.6 | 20.4 | 2.3 | 3.9 | 1631 | ||
| Togo | Children | PCV-hv | PCV13(2014) | 1111 | 2014-2016 | 60.0 | 40.0 | ||||
| Zambia | Children | PCV-hv | PCV10(2013) | 4033 | 2014-2019 | 52.0 | 2.0 | 50 | |||
| 多国 | Children | Hybrid Period | Pre-PCV, PCV-hv | 3261 | 2010-2016 | 33.5 | 4.1 | 62.4 | 370 | ||
| EMRO | Kuwait | All Ages | PCV-hy | PCV13(2010) | 2771 | 2010-2013 | 28.9 | 26.7 | 33.3 | 1.1 | 45 |
| Morocco | Children | PCV-hv | PCV13(2011), PCV10 2012) | 807 | 2011-2014 | 95.9 | 4.1 | 68 | |||
| Oman | Children | PCV-hv | PCV13(2012) | 1290 | 2014-2016 | 25.7 | 22.9 | 51.4 | 35 | ||
| Adults | PCV-hv | PCV13(2012) | 1290 | 2014-2016 | 40.0 | 3.3 | 51.7 | 60 | |||
| All Ages | PCV-hv | PCV13(2012) | 1290 | 2014-2016 | 32.4 | 8.1 | 59.5 | 37 | |||
| Pakistan | Children | PCV-hv | PCV10(2012) | 916 | 2013-2017 | 21.7 | 78.3 | 92 | |||
| All Ages | Hybrid Period | Pre-PCV, PCV10(2012) | 3275 | 2005-2013 | 42.3 | 5.4 | 14.4 | 37.8 | 111 | ||
| Qatar | All Ages | Transitional Period | PCV7(2005) | 302 | 2005-2009 | 77.9 | 7.4 | 12.3 | 2.5 | 122 | |
| Saudi Arabia | Children | Hybrid Period | PCV7(2009), PCV13 (2010) | 19 | 2009-2012 | 84.6 | 2.6 | 6.4 | 6.4 | 78 | |
| All Ages | Hybrid Period | Pre-PCV, PCV7(2009), PCV13(2010) | 2772 | 2000-2016 | 91.7 | 7.9 | 9.0 | 8.7 | 277 | ||
| WPRO | Cambodia | Children | Hybrid Period | Pre-PCV, PCV13(2015) | 3514 | 2012-2018 | 86.4 | 13.6 | 22 | ||
Singapore | Adults | PCV-hv | PCV13(2011) | 554 | 2012-2017 | 71.4 | 1.1 | 12.7 | |||
| All Ages | Transitional Period | Pre-PCV, PCV13(2011) | 689 | 1997-2013 | 70.5 | 7.4 | 16.9 | 5.2 | 757 | ||
| Taiwan, China | Children | Transitional Period | PCV7(2005)/PCV13 (2015) c | 191 | 2013-2014 | 80.5 | 5.5 | 13.9 | 36 | ||
| PCV-hv | PCV13(2015) | 2590 | 2015-2017 | 39.0 | 9.3 | 51.7 | 205 | ||||
| Adults | Hybrid Period | PCV7(2005)/PCV13 2015) c | 599 | 2011-2015 | 66.0 | 1.3 | 18.0 | 4.7 | 50 | ||
| PCV-hv | PCV13(2015) | 189 | 2017-2020 | 44.7 | 9.7 | 41.8 | 3.8 | 237 | |||
| All Ages | Transitional Period | PCV7(2005)/PCV13 (2015) c | 3399 | 2012-2014 | 76.9 | 7.7 | 15.4 | 1.0 | 104 | ||
| Hybrid Period | PCV7(2005)/PCV13 2015) c, PCV13(2015) | 182 | 2013-2017 | 57.8 | 17.5 | 23.8 | 1.0 | 206 | |||
| PCV-hv | PCV13(2015) | 3702 | 2016-2018 | 44.4 | 16.2 | 33.3 | 6.1 | 99 | |||
| PCV13: Serotypes covered by both PCV7 and PCV13: 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 19F, 18C, 23; Serotypes additionally covered by PCV13 compared to PCV7: 1, 5, 7F, 3, 6A, 6A/6B, 19A PCV20: PCV20(22F, 33F, 8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B, 15C, 15B/C, 15B/15C). Non-PCV20: Refers to serotypes specific to PPSV23 (2, 9N, 17F, 20, 20A, 20B) and NVST. Non-vaccine serotypes: Indistinguishable, unrecognizable serotypes. PCV-hv: Higher valent PCV vaccination period. For example: PCV10 or PCV13 as the latest vaccine applied in the national immunization schedule. *Data extracted from percentage numbers, the sum of percentages may not always equal 100%. a Hounde and Kaya Region. b Titao Region. c catch-up vaccination for older children (Source:Fletcher, M. A., Daigle, D., Siapka, M., Baay, M., Hanquet, G., & Morales, G. D. C. (2024). Serotype distribution of invasive pneumococcal disease from countries of the WHO Africa, Americas, Eastern Mediterranean, South-East Asia, and Western Pacific regions: A systematic literature review from 2010 to 2021. Frontiers in Public Health, 12.) | |||||||||||
Currently available pneumococcal vaccines include the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPV) and the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV), which cover the most common serotypes causing PD. The serotypes covered vary among different vaccines (Figure 3).
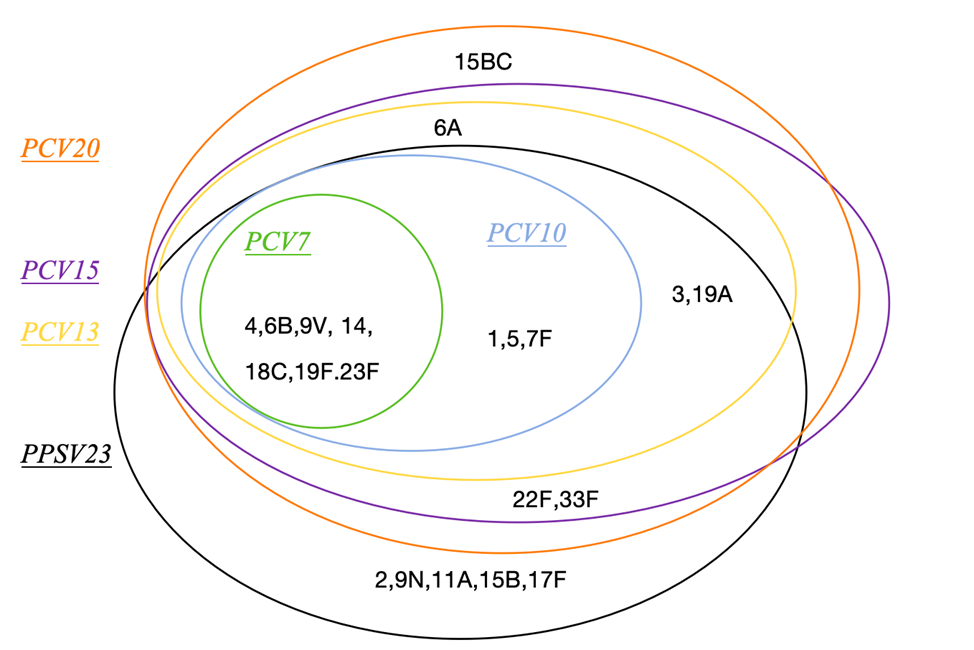
Source: Liu, X., & Chen, M. (2022). Carbohydrate-based vaccines of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 62(2), 446–457.
Content Editor: Tianyi Deng, Ziqi Liu
Page Editor: Ziqi Liu
References
- Weiser, J.N., Ferreira, D.M. & Paton, J.C. Streptococcus pneumoniae: transmission, colonization and invasion. Nat Rev Microbiol 16, 355-367 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0001-8
- Yahiaoui RY, den Heijer CDj, van Bijnen EM, Paget WJ, Pringle M, Goossens H, Bruggeman CA, Schellevis FG, Stobberingh EE; APRES Study Team. Prevalence and antibiotic resistance of commensal Streptococcus pneumoniae in nine European countries. Future Microbiol. 2016 Jun;11:737-44. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2015-0011. Epub 2016 May 18. PMID: 27191588.
- CDC. Pinkbook: Pnumococcal Disease. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/pneumo.html#epidemiology. Accessed December 31, 2021.
- Chinese Preventive Medicine Association; Vaccine and Immunization Branch of the Chinese Preventive Medicine Association. Expert consensus on immunoprophylaxis of pneumococcal diseases (2020 edition). Chinese Journal of Epidemiology. 2020;41(12):1945–1979. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20201110-01353
- Yao Kaihu. Overview of the burden of pneumococcal diseases in China. Chinese Medical Journal. 2020;100(42):3363–3366. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20200825-02462
- Brooks Lavida R K,Mias George I. Streptococcus pneumoniae’s Virulence and Host Immunity: Aging, Diagnostics, and Prevention.Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 1366.DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01366
- CDC. Pneumococcal Disease: Risk Factors for Clinicians. https://www.cdc.gov/pneumococcal/clinicians/risk-factors.html. Accessed December 31, 2021.
- National Clinical Research Center for Respiratory Diseases, National Center for Children’s Health, Respiratory Group of the Chinese Medical Association Pediatrics Branch, et al. Expert consensus on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of pediatric pneumococcal diseases in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Pediatrics, 2020, 35(07): 485-505. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn101070-20200306-00329
- CDC. Pneumococcal Disease Transmission: For Clinicians. https://www.cdc.gov/pneumococcal/clinicians/transmission.html. Accessed December 31, 2021.
- Johnson HL, Deloria-KM, Levine OS et al. Systematic evaluation of serotypes causing invasive pneumococcal disease among children under five: the pneumococcal global serotype project. PLoS Med. 2010,7(10):e1000348. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000348.
- Jauneikaite, E., Jefferies, J. M., et al. Prevalence of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes causing invasive and non-invasive disease in Southeast Asia: a review. Vaccine. 2012,30(24), 3503–3514.
- Chen Y, Deng W, Wang SM, et al. Burden of pneumonia and meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in China among children under 5 years of age: a systematic literature review[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(11): e27333. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027333
- Men, W., Dong, Q., Shi, W. et al. Serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance patterns of invasive pneumococcal disease isolates from children in mainland China—a systematic review. Braz J Microbiol.2020,51(2): 665–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-019-00198-9





