Currently available pneumococcal vaccines include Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine (PPV) and Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV).
PPV vaccine
The protective effect of the early 4-valent pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide vaccine was demonstrated in 1945. In 1977, the United States successfully developed the 14-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPV14), which was approved for market by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1978. In 1983, the U.S. pioneered the development of the PPV23, which was widely used and covered the following serotypes: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6B, 7F, 8, 9N, 9V, 10A, 11A, 12F, 14, 15B, 17F, 18C, 19A, 19F, 20, 22F, 23F, and 33F. Currently, there are six types of PPV23 approved for use in China, which are manufactured by Merck Sharp & Dohme (China) Ltd., Chengdu Institute of Biological Products Co., Ltd., Yuxi Walvax Biotechnology Co. Ltd., Kangtai Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Sanofi Pasteur Biological Products Co., Ltd., and Beijing Zhifei Lvzhu Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Table 1).
Table 1 Approved PPV23 Vaccines in China as of 20242
| Product Name | Wo Duo Fei | Hui Yi Kang | Wei Min Fei Le | Pneumo23® | Pneumovax® | You Wei Ke |
| Type | PPV23 | PPV23 | PPV23 | PPV23 | PPV23 | PPV23 |
| Producers | Yuxi Walvax | Chengdu Institute of Biological Products | Beijing Minhai Biotechnology | Sanofi Pasteur Biological | Merck Sharp & Dohme | Beijing Zhifei Lvzhu |
| China Launch Date | 2017 | 2006 | 2018 | 2014 | 2011 | 2023 |
| Approved Population in China | High-risk individuals aged 2 years and above | > 2 years old | High-risk individuals aged 2 years and above | High-risk individuals aged 2 years and above | High-risk individuals aged 2 years and above | High-risk individuals aged 2 years and above |
| Coverage of Serotypes | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6B, 7F, 8, 9N, 9V, 10A, 11A, 12F, 14, 15B, 17F, 18C, 19A, 19F, 20, 22F, 23F and 33F | |||||
| Vaccination dose | 1 dose | |||||
| Vaccination Schedule | 1 dose for routine vaccination. 5 years between revaccination for high-risk groups and 3-5 years between revaccination for children under 10 years of age with nephrotic syndrome, splenectomy and sickle cell disease | |||||
PCV Vaccine
PCVs approved for use worldwide include PCV7, PCV10, PCV13, PCV15, PCV20, and PCV21. PCV7 was successfully developed by Wyeth (acquired by Pfizer in 2009) in 2000 and approved for marketing in the U.S. It contains serotypes 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, and 23F, and has been replaced by PCV13. PCV10 was developed by GlaxoSmithKline in 2009 and approved for marketing in the EU. The first PCV13 was developed by Pfizer (formerly Wyeth) and approved by the United States in 2010. In recent years, higher valent PCV vaccines were launched in the market. In June 2021, U.S. FDA approved Pfizer’s pneumococcal 20-valent conjugate vaccine for adults ages 18 years or older. Following this approval, the pneumococcal 15-valent conjugate vaccine (VAXNEUVANCE™) developed by MSD was launched in the U.S. market in July 2021. In June 2024, the U.S. FDA approved another adult PCV developed by MSD – the CAPVAXIVE™ (Pneumococcal 21-valent conjugate vaccine) for prevention of invasive pneumococcal disease and pneumococcal pneumonia in adults.
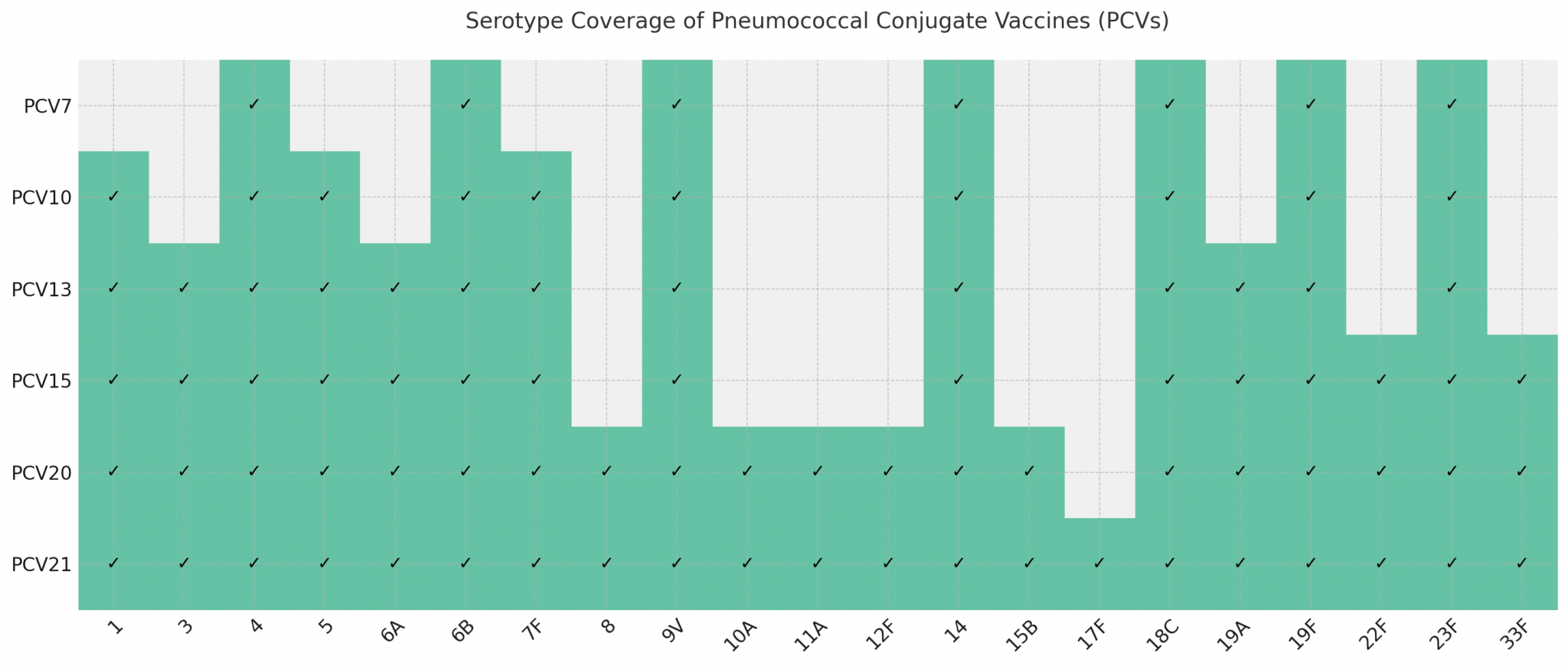
There are currently four types of PCV13 available in China, produced by Pfizer (approved in 2016), Yuxi Walvax Biotechnology Co. Ltd (approved in 2020), Beijing Minhai Biological Products Co. Ltd (approved in 2021), and CanSino Bio Co. Ltd (approved in 2025) (Table 2).
Table 2 PCV13 vaccines approved for use in China 2
| Product Name | Prevenar 13 | Wo An Xin | Wei Min Fei Bao | You Pei Xin |
| Type | PCV13 | PCV13 | PCV13 | PCV13i |
| Producers | Pfizer | Yuxi Walvax | Beijing Minhai | CanSino |
| Global Availability | 2010 | – | – | – |
| China Launch Date | November 2016 | March 2020 | October 2021 | June 2025 |
| Approved Population in China | Children aged 6 weeks to 5 years | |||
| Coverage of Serotypes | 1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19A, 19F and 23F | |||
| Vaccination Schedule (Infants under 6 months of age) | For infants aged 6 weeks to 6 months: A total of four doses is recommended. The primary immunization consists of one dose each at 2, 4, and 6 months of age, followed by a booster dose at 12–15 months. The first dose of the primary series may be administered as early as 6 weeks of age, with subsequent doses given at intervals of 1 to 2 months. | For infants aged 2–6 months (minimum 6 weeks of age): A total of four doses are recommended. The first dose is preferably administered at 2 months of age (minimum 6 weeks). Three primary doses are given at 2-month intervals, followed by a booster dose at 12–15 months of age. Alternative schedule starting at 3 months of age: Three primary doses are administered at 1-month intervals, followed by a booster dose at 12–15 months of age. | For infants aged 2 to 6 months (minimum 6 weeks of age): A total of four doses is recommended. The first dose should be administered at 2 months of age (minimum 6 weeks), followed by three primary doses at 2-month intervals. A fourth booster dose should be given between 12 to 15 months of age. | |
| Vaccination Schedule (Infants over 6 months of age) | Infants aged 7–11 months: A total of three doses are recommended. The second dose should be given at least one month after the first. A third (booster) dose should be administered after 12 months of age, at least two months after the second dose.Children aged 12–23 months: A total of two doses are recommended, administered at an interval of at least two months.Children aged 2–5 years (before the 6th birthday): A single dose is recommended. | |||
PCVs work by covalently binding the polysaccharides of the pneumococcal capsule to proteins, transforming the polysaccharide antigens from being T-cell independent to T-cell dependent. This allows infants to mount a robust antibody response and develop immunological memory after vaccination. Domestic and international immunization programs are mostly used for infants and young children, for example, the United States and Canada use the “3+1” schedule (2, 4, 6, 12 months of age), Australia uses the “3+0” schedule (2, 4, 6 months of age). UK has changed its PCV schedule from “2+1” to “1+1” in 2020 (12 weeks and 12 months of age) as a maintenance immunization strategy following the significant reduction of PCV-serotype IPD 3. In contrast, PPVs are T-cell-independent antigens and generally ineffective in eliciting protective antibody responses in children under 2 years old. The response levels to different serotypes can also vary among individuals. PPVs are primarily used for adults’ vaccination. The efficacy of PPV23 in preventing invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) decreases with age, being highest in individuals under 55 years old and lowest in those aged 85 and above 4.
Content Editor: Xiaotong Yang, Ziqi Liu
Page Editor: Ziqi Liu
References
- Chinese Society of Preventive Medicine, Chinese Society of Preventive Medicine, Division of Vaccines and Immunization. Expert consensus on immunoprophylaxis of pneumococcal diseases (2020 edition). Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2020, 54(12):1315-1363.
- All from the company’s official website
- Bertran, M., D’Aeth, J. C., Abdullahi, F., et al. (2024). Invasive pneumococcal disease 3 years after introduction of a reduced 1 + 1 infant 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine immunisation schedule in England: a prospective national observational surveillance study. The Lancet. Infectious diseases, 24(5), 546–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00706-5
- Shapiro ED, Berg AT, Austrian R, et al. The protective efficacy of polyvalent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. The New England J Medicine, 1991, 325 (21):1453-1460.





